USA
800 691 9120
UK
01225 704844
We use cookies on our website to analyze website usage and to help secure the website against misuse. Advertising and functional cookies are not used in our site or our web application products.
By clicking “Accept Essential Cookies Only”, you consent to us placing these cookies.
This guide explains which assets you must depreciate, which you must write off, and which offer a choice between the two. These decisions impact your profit and loss (P&L) and corporation tax.
In the USA, the document IRS 946 - How to Depreciate Property provides detailed information on depreciation methods and rules.
The above document also provides tables (MACRS and ADS) for calculating depreciation amounts for different asset classes. These tables can actually be derived with simple formulae, or you can use the tables.
In the UK, businesses don’t use depreciation for tax purposes. Instead, they claim capital allowances, which provide tax relief for capital expenditure. Capital allowances reduce taxable profits, whereas depreciation affects only the accounting books. Documents from the UK government include:
When you depreciate, only a part of the value of the asset is subtracted from your profits each year, so if you are using straight line depreciation over 5 years, 20% of the asset cost is moved from your balance sheet to your P&L as a loss. The rest of the value of the asset stays on your balance sheet.
When you write off, all of the cost of the asset goes straight to your P&L as a loss.
Depreciation spreads the cost of an asset over its useful life. You must depreciate assets that:
Examples:
IRS rules require depreciation for these assets using methods like straight-line or declining balance, based on their assigned recovery periods.
A write-off deducts the entire cost of an asset in the year it’s purchased or deemed worthless. You must write off assets that:
Examples:
These expenses are deducted immediately as they don’t meet depreciation criteria.
Some assets qualify for either depreciation or write-off. These include:
In the USA, additional rules allow expensing of assets at purchase, these are covered in more detail in the IRS 946 document:
This example compares depreciation and write-off for a $10,000 computer system using a 5 year recovery period, straight line, and 21% corporate tax.
| Year | Depreciation | Section 179 Write-Off |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
$2,000 expense Tax savings: $2,000 × 21% = $420 |
$10,000 expense Tax savings: $10,000 × 21% = $2,100 |
| 2 | $2,000 expense Tax savings: $420 | $0 |
| 3 | $2,000 expense Tax savings: $420 | $0 |
| 4 | $2,000 expense Tax savings: $420 | $0 |
| 5 | $2,000 expense Tax savings: $420 | $0 |
| Total | $10,000 expense Tax savings: $2,100 over 5 years | $10,000 expense Tax savings: $2,100 in Year 1 |
The choice of depreciation vs write-off depends on your financial situation:
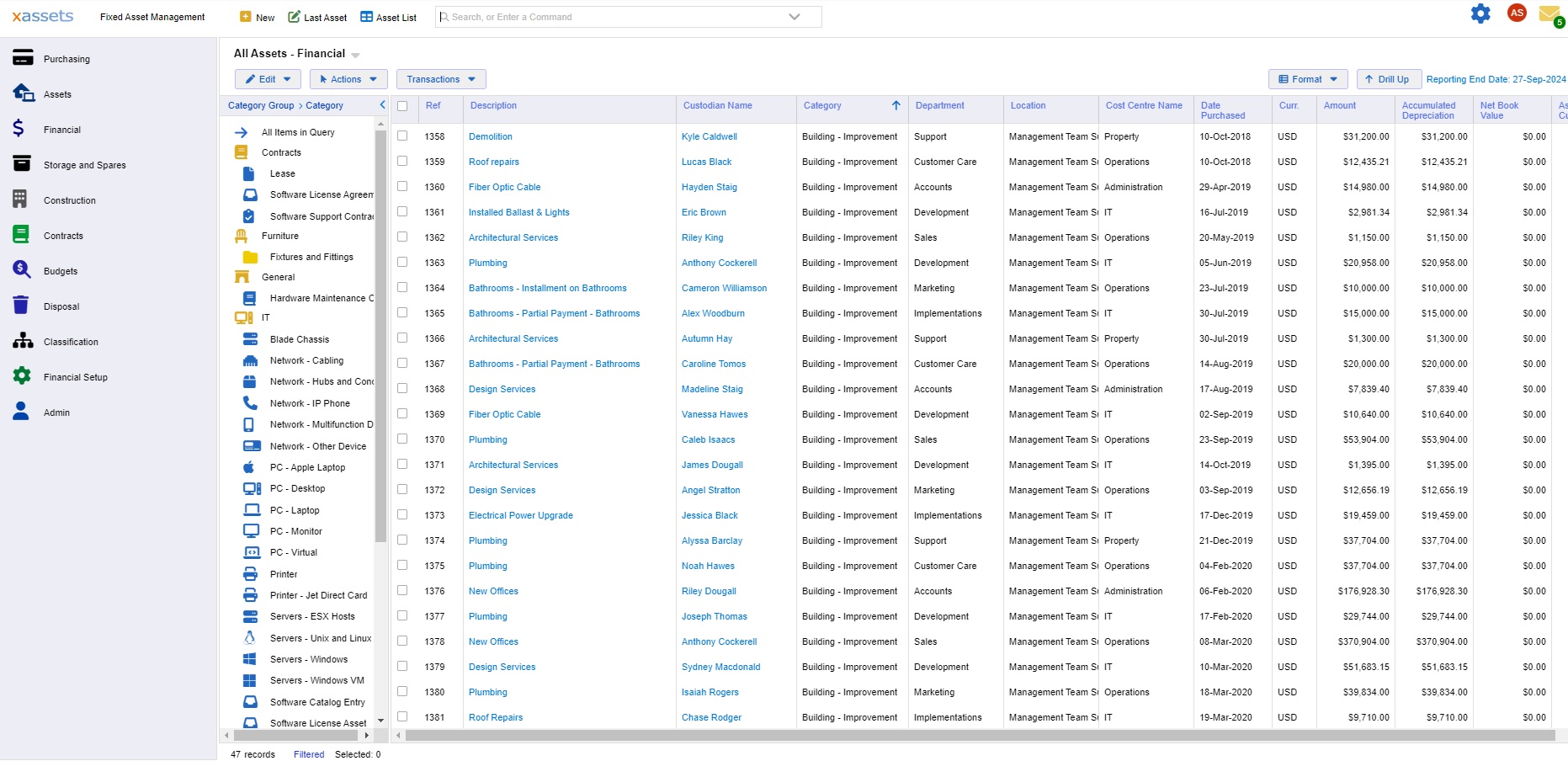
xAssets Fixed Asset Management Software includes a comprehensive multi-currency, multi-book depreciation calculation engine with configurable formulae and table lookups. The MACRS tables are built into the product (and can be modified), or you can replicate the MACRS table numbers with double declining balance and straight line formulae. The system supports all types of depreciation and supports complex setups with multiple sets of accounting periods. The system works with unusual accounting period setups such as 4-4-5, and also supports accounting period changes (e.g. a change of the financial year end period). You can read more about the specifics of the depreciation engine here
The system has passed USAF DoD security checks and is scalable to very large enterprises. Annual calculation of 50,000 assets in four parallel accounting books (to create 2.4 million monthly transactions) was recently timed in a scalability test at 6 minutes, and for many smaller customers, calculations are instantaneous.
The decision to depreciate or write off assets has a large effect on corporation tax. Use depreciation for long-term high value assets and write-offs for short-term or low value items. Section 179 allows write off for qualifying property.
Free instances are free forever and can show demo data or your data.